What is WPC Board
WPC (Wood Plastic Composite) is a hybrid material. 100% waterproof and termite-proof, making it perfect for bathroom cabinets and decks.
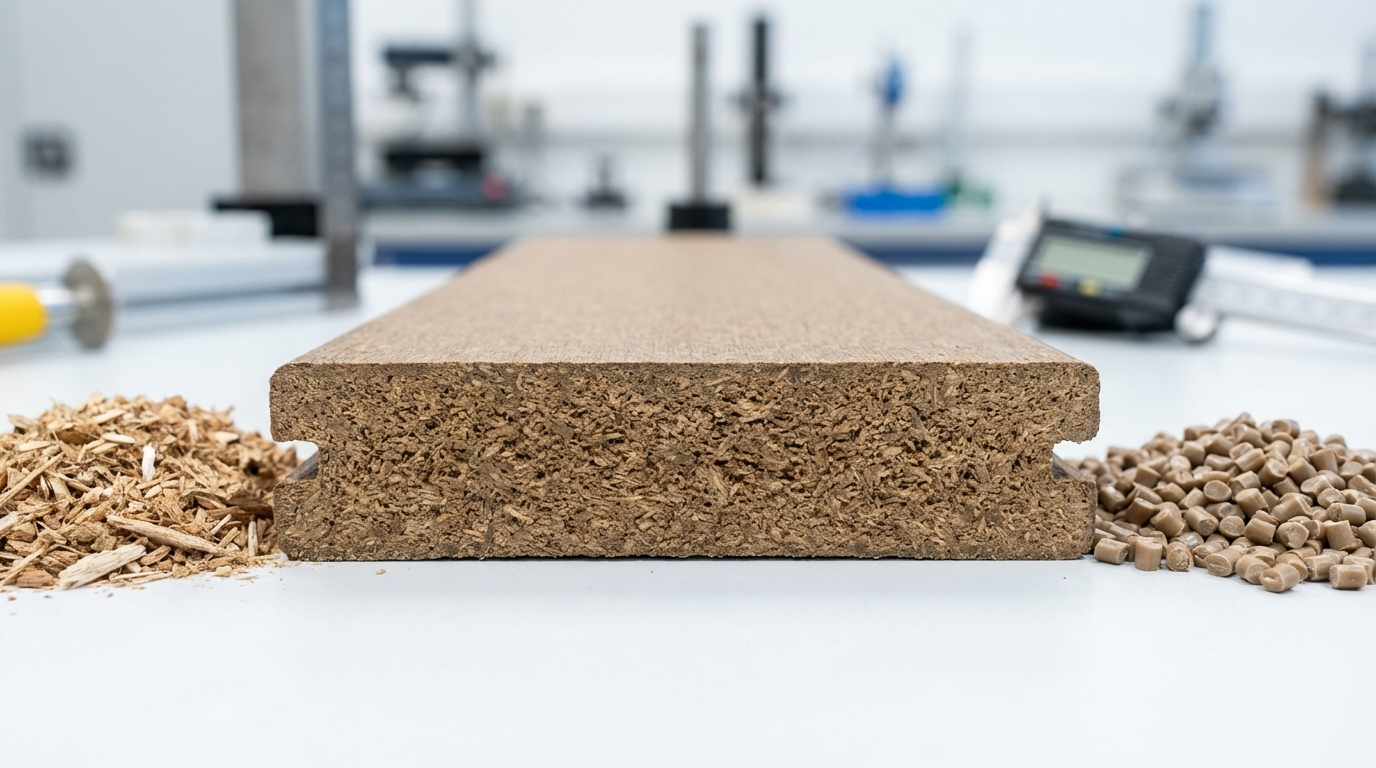

What Makes WPC Board a Hybrid Material?
Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) board combines natural wood fibers with synthetic polymers, creating a material that draws strengths from both worlds. At its core, WPC consists of wood flour—finely ground wood particles derived from wood waste or agricultural residues—blended with thermoplastics like PVC or polyethylene. This mixture, typically 40-70% wood by weight, is compounded with additives such as stabilizers, lubricants, and colorants.
The manufacturing process involves extrusion, where the heated blend is forced through a die to form sheets or profiles. This results in a dense, uniform board unlike traditional plywood's layered veneers or MDF's resin-bound fibers. In India, where wood waste from sawmills and rice husks is abundant, WPC leverages local resources, reducing reliance on imported timber amid rising deforestation concerns.
Core Properties: Waterproofing and Termite Resistance Explained
WPC's defining traits stem from its composition. The plastic matrix encases wood fibers, preventing water absorption—even submersion tests show negligible swelling compared to plywood's 10-20% rate in humid conditions. This makes it effectively 100% waterproof for practical use, ideal for India's monsoon-heavy regions like Kerala or coastal Maharashtra.
Termite-proofing arises because the plastic coating denies pests access to cellulose in the wood fibers. Unlike untreated plywood vulnerable in termite-prone Gangetic plains, WPC requires no chemical preservatives. Other properties include:
- Dimensional stability: Minimal warping in 80-90% humidity swings common in Indian interiors.
- Low thermal expansion: Better than pure plastics for flooring.
- Moderate fire resistance: Self-extinguishing grades available, though not as robust as cement boards.
Drawbacks include lower screw-holding strength than solid wood, addressed by pilot holes or inserts in modular furniture.
Common Applications in Indian Construction and Interiors
WPC excels where moisture and pests challenge wood. Bathroom cabinets top the list—vanity units withstand steam and splashes without delamination, unlike MR-grade plywood. Kitchen shutters in humid apartments fare similarly, often finished with laminates for aesthetics.
Outdoor decks and cladding suit balconies or poolside areas, resisting rain without painting. False ceilings in bathrooms or garages use WPC profiles for ventilation gaps. In commercial setups like hospitals or hotels, partitions benefit from its hygiene—non-porous surfaces deter mold.
Contractors favor WPC for quick installs via screws or adhesives, cutting labor in high-rise projects. Homeowners in Mumbai chawls or Delhi basements opt for it over costly marine plywood.
WPC Board vs. Plywood, MDF, and HDHMR: A Practical Comparison
| Property | WPC Board | MR Plywood | BWR Plywood | MDF | HDHMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | 100% waterproof | Poor (interior only) | Moderate (boiling not sustained) | Poor | Moderate (humid interiors) |
| Termite Resistance | High (plastic barrier) | Low (needs treatment) | Moderate | Low | High (resins) |
| Moisture Swell (%) | <1% | 15-20% | 8-12% | 10-15% | 5-8% |
| Best For | Wet areas, outdoors | Dry interiors | General use | Carving, painting | Humid kitchens |
| Weight (per sqm, 18mm) | Medium | Heavy | Heavy | Medium | Medium |
This table highlights why architects specify WPC for zones plywood can't handle, though HDHMR competes in kitchens at similar costs.
Quality Indicators and Standards in the Indian Market
India lacks a dedicated ISI mark for WPC, but reputable producers align with IS 15444 for PVC profiles or general plastic composites. Check for density (0.9-1.2 g/cm³ for rigidity), formaldehyde emission (E0/E1 levels), and certifications like GREENGUARD for low VOCs.
Visual cues: Uniform color sans knots, smooth edges post-extrusion. Test samples by soaking—quality WPC stays rigid. Regional variations: South India (Tamil Nadu factories) emphasizes UV-stabilized outdoor grades; North focuses on indoor thicknesses (6-25mm).
Cost Drivers and Purchase Logic for Buyers
WPC pricing hinges on wood-plastic ratio, thickness, and additives—thinner 8mm sheets for cabinets cost less per square meter than 18mm structural boards. Imported plastics inflate northern prices versus south's local sourcing. Expect relative costs 20-50% above MR plywood but below marine grades, varying by dealer markups (10-30%).
Contractors buy bulk from wholesalers for volume discounts; homeowners source via interior shops. Factor lifecycle: WPC's 15-20 year span offsets upfront costs in wet zones. Avoid unbranded stock—opt for traceable suppliers with warranties.
Installation Best Practices and Long-Term Care
Pre-drill for screws to prevent cracking; use PVC-compatible adhesives like solvent cement. Seal edges in high-humidity spots. Maintenance involves mild soap wipes—no polishing needed, unlike wood.
In India's dust-laden air, vacuum grooves yearly. For decks, UV-protected variants extend fade-free life to 10+ years.
Frequently Asked Questions on WPC Boards
Is WPC board suitable for load-bearing walls?
No—it's non-structural. Use for cladding or partitions over frames.
Can WPC be painted or laminated?
Yes, with primers for paint; laminates bond well via hot-pressing.
How does WPC perform in extreme heat?
Stable up to 60°C; softens above 80°C, less issue than pure PVC.
Is WPC eco-friendly?
Recycles wood waste and plastics, but PVC variants raise disposal queries—PE-based options greener.
What's the thickness range available?
4-40mm sheets; 8-18mm common for cabinets and furniture.
Want Plywood Suggestions?
Share a few details and a PlyPrice specialist will suggest suitable brands and connect you to responsive dealers.