What is ACP Sheet
ACP (Aluminium Composite Panel) is a lightweight cladding material. Used for modern building facades, signage, and exterior branding.
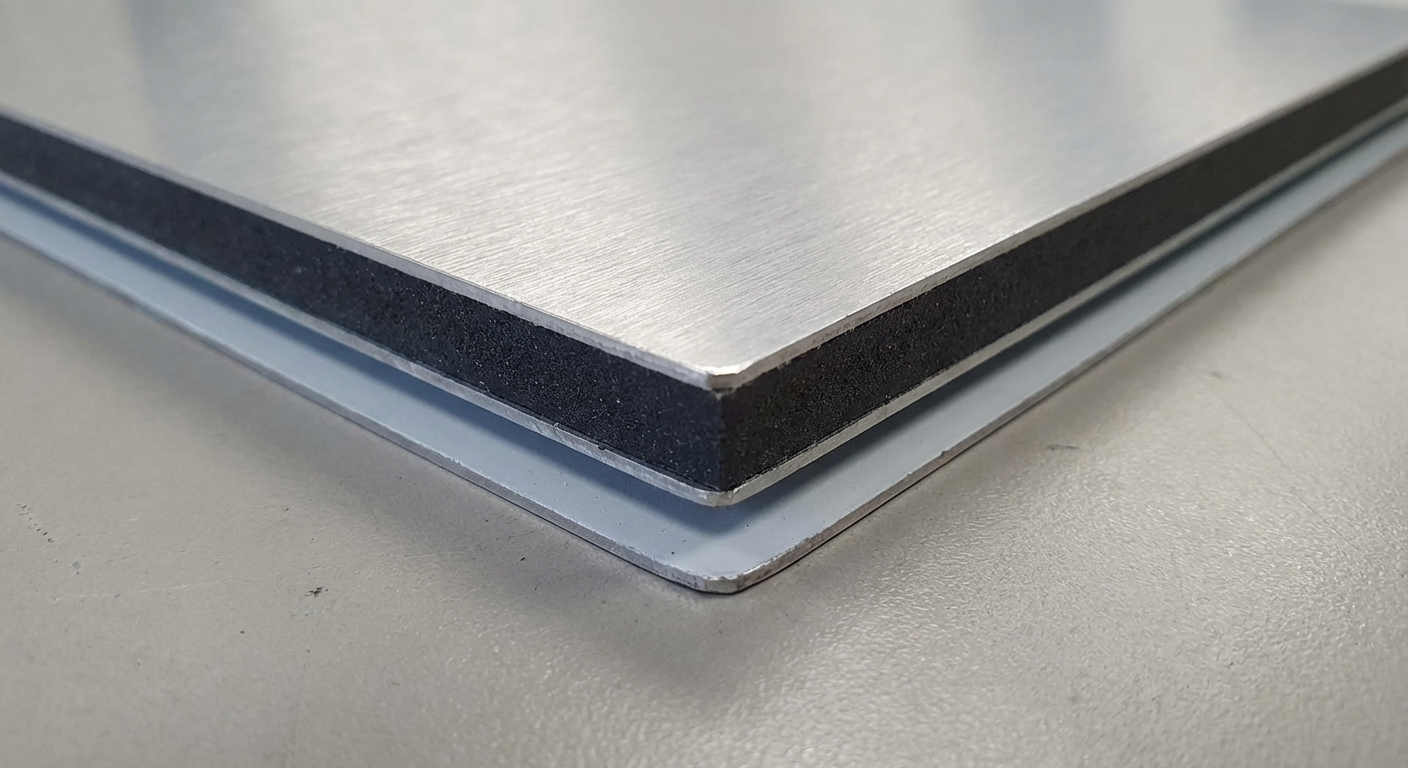
What Exactly is an ACP Sheet?
ACP, or Aluminium Composite Panel, refers to a rigid, flat sheet formed by bonding two thin aluminium sheets to a non-aluminium core material, typically through a continuous lamination process under controlled heat and pressure. This sandwich-like construction delivers a lightweight yet durable surface ideal for exterior and interior applications where traditional heavy materials like stone or metal cladding prove impractical.
In practical terms, ACP sheets function as a versatile cladding solution, combining the malleability of aluminium with core stability to withstand environmental stresses. Unlike solid metal panels, the composite design reduces weight by up to 80% while maintaining flatness and rigidity, making it a go-to choice for modern Indian construction where speed and cost-efficiency matter.
Core Composition: Breaking Down the Layers
From first principles, ACP's effectiveness stems from its three-layer architecture:
- Top and bottom aluminium skins: Usually 0.1-0.5 mm thick, these provide weather resistance, UV protection, and a printable surface. High-purity aluminium (often alloyed for strength) forms the outer barrier against corrosion.
- Core material: The middle layer, 2-6 mm thick, dictates fire performance and rigidity. Common cores include polyethylene (PE) for general use, or fire-retardant mineral-filled polymers (FR grade) for safety-critical areas.
- Adhesive bonding: Polyethylene or polyurethane glues ensure delamination resistance under thermal expansion.
This setup allows ACP to flex slightly without cracking, unlike brittle alternatives, which is crucial in India's seismic zones and temperature swings from 5°C winters to 45°C summers.
Primary Applications in Indian Building Practices
ACP sheets excel in scenarios demanding lightweight, aesthetic coverings. Key uses include:
- Building facades: Cladding high-rises, malls, and offices in cities like Mumbai, Delhi, and Bengaluru. The panels create sleek, curved, or flat elevations that mimic premium metal at lower structural load.
- Signage and branding: Retail storefronts, hoardings, and metro station displays leverage ACP's printability for vibrant digital prints resistant to fading in polluted urban air.
- Interior partitions and ceilings: False ceilings in hotels or partitions in commercial spaces, where fire-rated variants meet NBC (National Building Code) guidelines.
- Exterior branding: Villas in Tier-2 cities like Pune or Hyderabad use perforated ACP for privacy screens or feature walls that handle monsoon rains.
Contractors favor ACP for quick installation via aluminum framing systems, reducing labor by 30-40% compared to tile work.
ACP in India's Urban and Coastal Contexts
In humid coastal regions like Chennai or Goa, marine-grade ACP with enhanced anti-corrosive coatings prevents pitting from salt spray. Urban developers in NCR often specify PE-core for budget projects and FR-core for public buildings post-2010 fire safety regulations.
Types of ACP Sheets: Selecting by Grade and Core
| Type | Core Material | Typical Thickness | Best For | India-Specific Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard PE Core | Polyethylene | 3-4 mm | Signage, interiors | Cost-effective for non-fire zones; common in retail fitouts |
| Fire-Retardant (FR/A2) | Mineral-filled | 4-6 mm | Facades, high-rises | Mandatory for G+4+ buildings per local bylaws; tested to BS 476 |
| Anti-Bacterial | PE with silver ions | 3 mm | Hospitals, cleanrooms | Growing in post-pandemic healthcare projects |
| Nano/UV Resistant | Special coated PE | 4 mm | Coastal exteriors | Resists chalking in Rajasthan deserts or Kerala monsoons |
Thickness influences span capability—thinner for curves, thicker for large unsupported panels. Architects balance this with wind load calculations per IS 875 standards.
Advantages Driving ACP Adoption in India
- Lightweight efficiency: Reduces foundation loads, enabling taller structures on softer Mumbai soils.
- Design versatility: Digital printing supports custom colors, mimicking wood or stone without weight penalties.
- Low maintenance: Washable surfaces resist graffiti and dust in high-traffic Delhi markets.
- Thermal insulation: Core traps air, cutting AC loads by 10-15% in commercial spaces.
- Recyclable aluminium: Aligns with green building norms like GRIHA ratings.
Limitations and When to Avoid ACP
Despite popularity, ACP isn't universal. PE cores melt at high heat (not ideal near open flames), prompting FR mandates in public venues. Structural bowing occurs if framing gaps exceed 1 meter in windy Gujarat sites. High-gloss finishes scratch easily in DIY homeowner projects—better for pros. Alternatives like HPL sheets suit budget interiors, while zinc cladding handles extreme corrosion better.
Decision Factors for Buyers: Homeowners, Contractors, Architects
Homeowners (villas/bungalows): Prioritize 4 mm FR-grade for monsoons; check dealer warranties (5-15 years).
Contractors: Focus on panel size (1220x2440 mm standard) for minimal joints; source from certified fabricators to avoid peeling.
Architects/Designers: Specify PVDF coatings for 20-year color retention; verify core density (>1600 kg/m³ for FR).
Cost drivers: Core type (PE lower, FR 20-50% higher), thickness, and import vs local (South Korea/China origins common). Regional variation—cheaper in Gujarat hubs, premium in Northeast due to logistics.
Installation Essentials in Indian Conditions
ACP fixes via wet (silicone sealant) or dry (rivets/clips) methods on galvanized frames. Key steps:
- Frame alignment to 2 mm tolerance.
- Panel expansion gaps (10 mm/m).
- Sealants for 100% water-tightness in Kerala rains.
Common pitfalls: Skipping fire barriers or using undersized fixings, leading to failures in cyclonic Odisha.
Maintenance and Longevity Insights
Annual pressure washing with mild detergent suffices. Inspect joints yearly for sealant cracks. Lifespan: 15-25 years in moderate climates, less near industrial effluents. Replace if core delaminates—visible as edge lifting.
ACP vs Alternatives: Quick Comparison
| Material | Weight | Cost Relative to ACP | Durability (India) | Use Case Edge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACP | Low | Baseline | Medium-High | Facades/Signage |
| Aluminium Sheets | Medium | 20-40% Higher | High | Pure Structural |
| Glass Facade | High | 2-3x Higher | High | Luxury Transparency |
| Stone Cladding | Very High | 50-100% Higher | Medium | Traditional Aesthetics |
Want Plywood Suggestions?
Share a few details and a PlyPrice specialist will suggest suitable brands and connect you to responsive dealers.


