What is Shuttering Plywood
Shuttering Plywood is densified, film-faced ply used for concrete formwork in construction. Highly durable and reusable. Learn more.
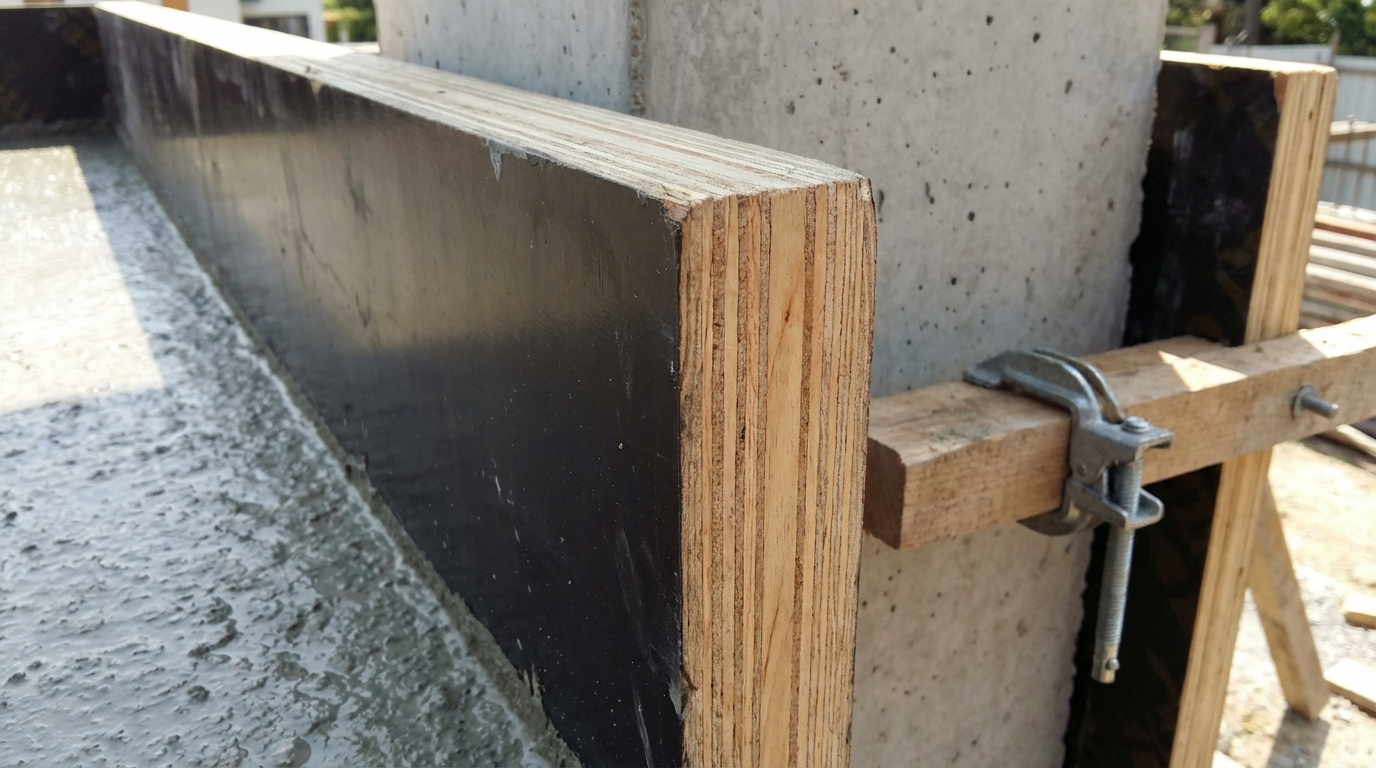

Core Definition and Purpose
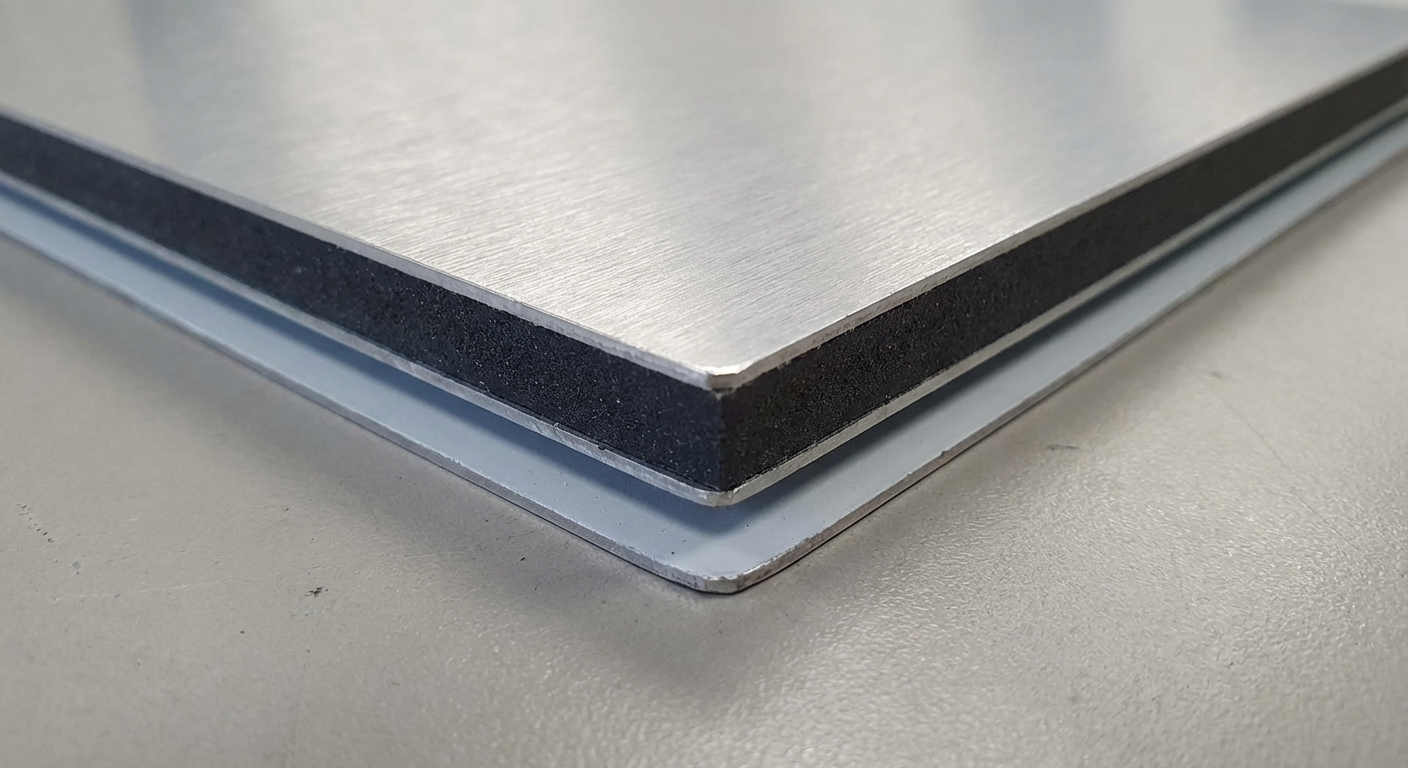
Shuttering plywood, also known as formwork plywood or concrete shuttering ply in Indian construction circles, starts as a engineered wood panel engineered specifically for temporary molds in reinforced concrete (RCC) pouring. Unlike standard plywood used for furniture or interiors, it undergoes densification—a process compressing the wood veneers under high pressure and heat to boost density and strength. This creates a rigid core capable of withstanding the hydrostatic pressure of wet concrete without warping or delaminating.
The defining feature is its film-facing: both faces receive a phenolic resin-impregnated overlay paper, fused under heat and pressure. This glossy, non-porous surface repels water, cement slurry, and concrete mix, ensuring easy release post-curing and minimal adhesion damage. In India's variable climates—from coastal humidity to northern dry heat—this combination addresses real-site challenges like monsoon delays and repeated pours.
Manufacturing Process from First Principles
Begin with hardwood veneers (often poplar or eucalyptus in India) rotated off logs and sorted by grain. Layers are glued with waterproof phenolic resins (WBP-grade adhesives), then pressed at 120-150 kg/cm² pressure—far exceeding regular ply's 10-20 kg/cm². Post-pressing, phenolic film sheets are applied to faces, cured at 140-160°C. Edges may get phenolic tape or resin sealing for extra water resistance.
This yields a panel typically 12mm to 18mm thick, balancing weight (around 40-50 kg per 8x4 sheet) for manual handling with structural load-bearing up to 800-1000 kg/m² in formwork setups. Indian mills follow IS:303 or enhanced processes, but verify via physical tests like boil-water resistance over lab certifications.
Primary Applications in Indian Construction
Shuttering plywood shines in formwork for columns, beams, slabs, and walls—ubiquitous in India's RCC-dominated building boom, from high-rises in Mumbai to rural housing under PMAY schemes. Panels assemble into reusable molds via props, ties, and clamps, containing concrete until it sets (typically 24-48 hours).
- Vertical formwork: Columns and shear walls, where uniform pressure demands flatness.
- Horizontal formwork: Slab shuttering over props, prioritizing span strength.
- Special uses: Staircases or curved elements with flexible thinner sheets.
Contractors favor it over steel forms for cost (initial outlay 20-30% lower) and ease in labor-intensive sites, though hybrid systems emerge in metro projects.
Durability Metrics and Reusability Potential
Durability hinges on cycles: quality shuttering ply endures 10-25 pours before surface wear or core degradation. Factors include:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan | India-Specific Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Face Film Quality | Thicker film (120-220 gsm) resists abrasion | Monsoon sites need 200+ gsm to counter slurry splash |
| Core Density | 0.75-0.85 g/cm³ prevents swelling | Test by edge soaking; coastal regions demand higher |
| Glue Line Strength | WBP adhesive survives 72-hour boils | ISI-marked for govt. tenders |
| Edge Sealing | Reduces moisture ingress | Tape edges post-cut for site longevity |
Reusability drops with poor site practices—over-tightening ties cracks edges, unclean release agents gum up films. Proper demolding (after 3-5 days), cleaning with water jets, and stacking flat extends life. In practice, contractors achieve 15+ cycles on budget variants, 20+ on premium.
How Shuttering Plywood Differs from Regular Grades
Standard MR or BWR ply fails in formwork due to lower density and untreated faces, absorbing moisture and delaminating under load. Shuttering ply's densified, film-faced build suits only heavy-duty exteriors—not interiors.
| Attribute | Shuttering Plywood | MR Plywood | BWR Plywood |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Concrete formwork | Interiors, furniture | General humid areas |
| Adhesive | WBP (boiling water proof) | MR (moisture resistant) | BWR (boiling water resistant) |
| Facing | Phenolic film both sides | Smooth paper overlay | Smooth paper overlay |
| Density | High (0.75+ g/cm³) | Medium (0.5-0.6 g/cm³) | Medium-high |
| Reusability | 10-25 cycles | Single-use | 3-5 uses |
| Load Capacity | High pressure tolerance | Low | Moderate |
BWP marine ply overlaps in waterproofing but lacks film, making it costlier and overkill for shuttering unless marine exposure applies.
Grading Standards and Quality Checks in India
No universal "shuttering grade" exists under BIS, but mills reference IS:4990 for formwork or enhanced IS:303. Look for:
- Uniform black/brown film without bubbles.
- Straight edges, no telegraphing (veneer show-through).
- Thickness tolerance ±0.5mm.
- Weight consistency per sheet.
Dealer tests: Hammer tap for delams, knife scratch for film integrity. Regional mills in Punjab, Gujarat dominate supply; northern variants suit dry sites, southern handle humidity better due to gum veneers.
Practical Buying Logic for Contractors and Builders
Purchase decisions pivot on project scale and budget. Small contractors opt 12mm for columns (lighter), large ones 18mm for slabs. Cost drivers: Film GSM, veneer quality, mill scale—expect 20-40% premium over BWR ply, varying by region (higher in metros due to logistics).
Decision tree:
- Budget sites: 10-15 cycle ply; stock 20% extra for losses.
- High-volume: Premium for 20+ cycles; negotiate bulk from mills.
- Verify: Sample test on-site pour; avoid unbranded imports prone to early peel.
Store vertically, film-out, under cover. Alternatives like plastic forms or Mivan systems cut reusability needs but raise upfront costs.
Want Plywood Suggestions?
Share a few details and a PlyPrice specialist will suggest suitable brands and connect you to responsive dealers.