What is HDF Board
HDF (High Density Fibreboard) is denser and harder than MDF. Used for heavy-duty flooring and applications requiring superior strength.
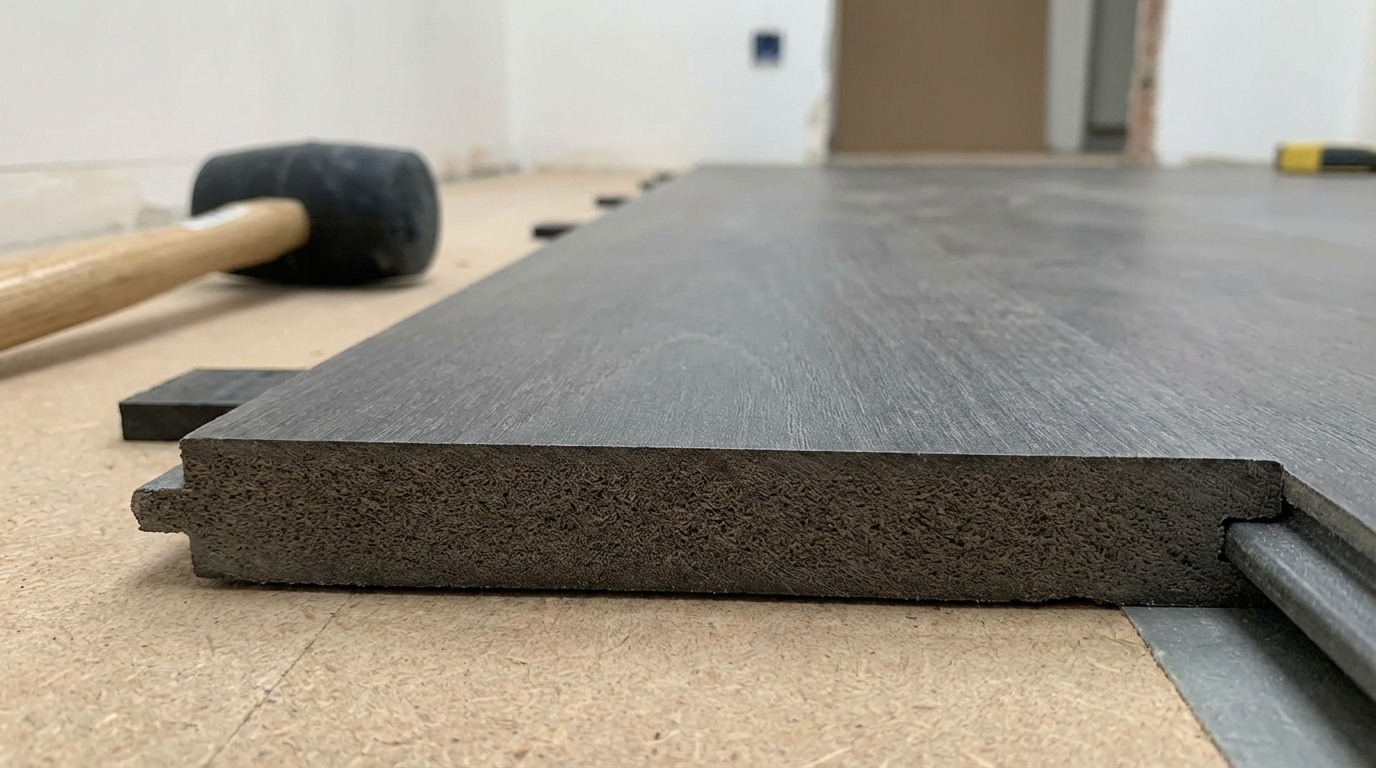

Defining HDF Board in Engineered Wood Context
High Density Fiberboard (HDF) emerges from the same family of engineered panels as MDF but through intensified manufacturing pressures. Wood fibers—typically sourced from fast-growing species like eucalyptus or poplar common in Indian plantations—are broken down, mixed with resins and waxes, then compressed at high temperatures exceeding 200°C and pressures up to 10 MPa. This process yields a panel with uniform density throughout, eliminating natural wood defects like knots or grain inconsistencies that plague solid timber in humid Indian conditions.
In practical terms, HDF's core distinction lies in its mass per unit volume, often reaching levels that make it feel substantially heavier and more rigid when handled at a dealer yard. This density arises from tighter fiber packing, creating a material suited for scenarios where surface loads demand unyielding support, unlike softer alternatives that might dent under everyday use.
Physical Properties Driving HDF's Performance
HDF panels exhibit a density profile that sets them apart, generally positioning them as the denser sibling in fiberboard hierarchies. This inherent trait translates to superior hardness, measured via metrics like Janka hardness tests, where HDF resists indentation far better than less compressed boards. For Indian contractors facing high-traffic installations, this means fewer callbacks for surface damage in entryways or commercial spaces.
Strength-wise, HDF holds fasteners like screws more securely due to its compressed structure, ideal for repeated assembly-disassembly in modular furniture setups popular among urban homeowners. While not inherently waterproof, its lower porosity reduces moisture ingress compared to looser boards, though coastal or monsoon-prone regions necessitate specialized grades.
Density and Hardness Benchmarks
- Density: Concentrated fiber arrangement results in boards that outweigh standard options by 20-40% at equivalent thicknesses.
- Hardness: Enhanced resistance to scratches and impacts, supporting thin veneers without telegraphing substrate flaws.
- Stability: Minimal expansion under load, critical in India's variable humidity swings from 30% in dry winters to 90% during rains.
HDF Versus MDF: Core Differences for Buyers
Buyers often encounter HDF positioned as an upgrade path from Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF), but the choice hinges on project demands rather than blanket superiority. MDF prioritizes machinability for intricate carvings or paint finishes, while HDF channels its energy into load-bearing resilience. In Indian workshops, MDF cuts smoother on CNC routers, but HDF endures better in final installations exposed to foot traffic or humidity.
| Attribute | HDF | MDF |
|---|---|---|
| Density Range | Higher (800+ kg/m³) | Medium (600-800 kg/m³) |
| Hardness & Strength | Superior screw-holding; impact-resistant | Adequate for light use; prone to dents |
| Moisture Behavior | Better inherent resistance; variants for wet areas | Swells faster without sealing |
| Machining | Firmer, requires sharper tools | Smoother cuts, less dust |
| Typical Thicknesses | 2.5-6 mm for flooring cores | 3-25 mm for cabinets |
| Cost Driver | 20-50% premium due to compression | Baseline affordability |
This comparison underscores why architects specify HDF for structural underlays in multi-story apartments, where MDF might suffice for wardrobe backs but falter under sustained weight.
Primary Applications: Heavy-Duty Flooring and Beyond
HDF shines in heavy-duty flooring, serving as the robust core beneath laminate or engineered wood tops. In Indian high-rises, where concrete subfloors meet vinyl overlays, HDF's density prevents sagging or telegraphing over time, accommodating underfloor heating trends in premium Delhi or Mumbai projects. Thicknesses around 8-12 mm provide the rigidity needed for click-lock systems that withstand monsoonal humidity without cupping.
Beyond floors, HDF supports demanding uses like door skins, wainscoting, and shop fittings. Contractors favor it for retail counters where constant loading from displays tests material limits. In furniture, slim HDF panels form tabletops or shelving in kitchens, leveraging strength without the weight penalty of blockboard.
India-Specific Use Cases
- Flooring underlays in humid metros like Chennai or Kolkata.
- Commercial interiors: Hotel lobby panels resisting trolley impacts.
- Modular kitchens: Base for high-moisture zones when in HMR form.
Moisture-Resistant Variants and Indian Climate Fit
Standard HDF improves on MDF's moisture profile through denser packing, but India's tropical climate demands upgrades like HDF-HMR (High Moisture Resistant) or HDHMR. These incorporate hydrophobic resins, enabling short-term exposure in bathrooms or utility areas without delamination. Homeowners in Kerala or Goa report longer service life with such boards versus plain MDF, though neither rivals BWP plywood for submersion.
Decision logic: Opt for certified HMR grades from mills adhering to voluntary standards when dealer assurances lack backing, as regional variations in resin quality affect outcomes.
Procurement Insights for Indian Buyers
Thickness dictates utility—thinner sheets (2-3 mm) suit decorative overlays, while 5-6 mm handles flooring rigors. Dealers in plywood hubs like Bhubaneswar or Indore stock HDF at premiums reflecting import reliance or specialized pressing lines, with costs scaling by moisture treatment and surface finish.
Verify panel edges for uniformity, as poor compression leads to crumbling during edging. Architects advise sampling from multiple suppliers, as northern mills emphasize density for cold storage fits, while southern ones prioritize humidity tweaks.
Limitations and Strategic Alternatives
HDF's rigidity can complicate on-site modifications without power tools, frustrating small-scale carpenters. It also generates more heat during sawing, posing edge-sealing challenges in uncoated forms. For ultra-wet zones, marine plywood remains preferable despite higher upfront outlay.
Choose MDF for cost-sensitive, low-wear cabinetry; HDF for anywhere strength trumps ease. In blended projects, layer HDF substructures under MDF faces for balanced performance.
Frequently Asked Questions on HDF Boards
Is HDF stronger than plywood?
HDF excels in uniform compression strength but lacks plywood's cross-grain tear resistance; select per load type.
Can HDF be used outdoors?
Not recommended without extensive sealing; interior applications align with its fiber composition.
How does HDF perform in Indian monsoons?
HMR variants hold up in intermittent exposure, but elevate off floors and seal joints for longevity.
What thickness of HDF for laminate flooring?
8-12 mm ensures stability over uneven Indian screeds; test for deflection under local spans.
Want Plywood Suggestions?
Share a few details and a PlyPrice specialist will suggest suitable brands and connect you to responsive dealers.