What is Fire Retardant Plywood
Fire Retardant Plywood is treated to delay fire spread and reduce smoke. Certified under IS:5509. Essential for safe kitchens and offices.

Defining Fire Retardant Plywood
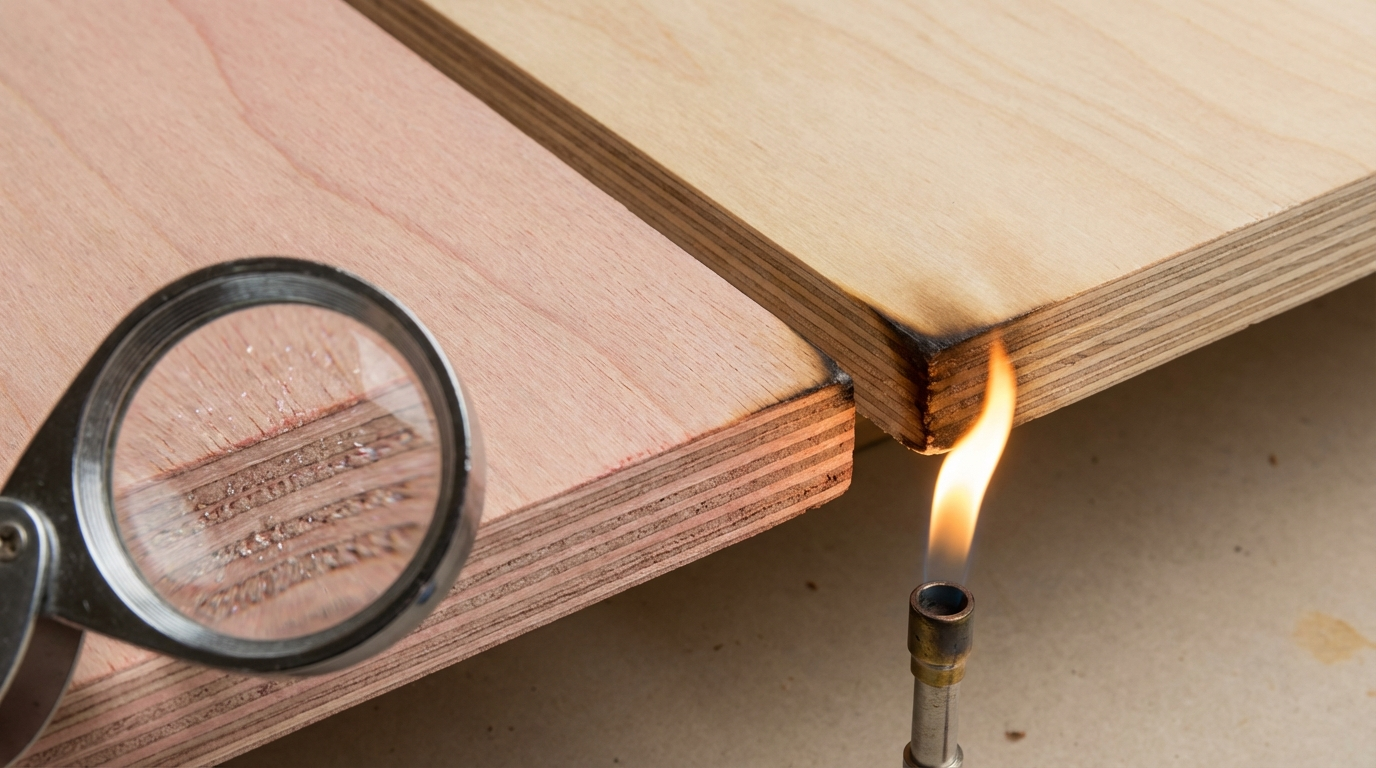
Fire retardant plywood refers to engineered wood panels treated with specialized chemicals to hinder ignition, slow flame propagation across the surface, and limit smoke emission during exposure to heat or fire. Unlike standard plywood, which combusts rapidly due to its cellulosic composition—releasing flammable gases through pyrolysis—these treatments promote char formation on the surface. This char layer acts as a barrier, insulating unburnt material underneath while releasing water vapor or non-combustible gases that dilute oxygen around the flame.
In practical terms for Indian users, this means panels that buy critical evacuation time in fire-prone settings, aligning with rising safety demands in urban apartments and commercial fit-outs amid frequent electrical faults and cooking-related incidents.
Core Mechanism: How Treatments Delay Fire Spread and Curb Smoke
At a fundamental level, untreated plywood ignites at around 250-300°C, with flames spreading via volatile vapors. Fire retardants disrupt this by endothermic reactions: chemicals like ammonium polyphosphate decompose, absorbing heat and forming intumescent chars. Borates or halogens further suppress radical chain reactions in the gas phase.
Smoke reduction stems from incomplete combustion inhibition; fewer soot particles form as the material chars rather than pyrolyzes fully. In India's humid coastal regions, where moisture accelerates wood degradation, these treatments must retain efficacy without leaching, typically limiting use to interior dry areas unless specified otherwise.
Treatment Processes for Fire Retardant Plywood
Compliance with Indian practices involves impregnation under vacuum-pressure cycles, forcing chemicals deep into veneers before gluing and hot-pressing. Key steps include:
- Pre-drying veneers to below 10% moisture for uniform uptake.
- Vacuum soaking in retardant solutions (e.g., Type 1: ammonium phosphate-based per IS 5509).
- Pressure application to achieve retention levels (e.g., 50-100 kg/m³ depending on thickness).
- Post-treatment drying and conditioning to stabilize dimensions.
This contrasts with surface coatings, which fail quickly; impregnation ensures performance through the panel's thickness, vital for modular furniture in high-traffic Indian offices.
IS 5509: India's Certification Standard Explained
IS 5509:2021 (third revision), issued by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), sets specifications for fire retardant plywood. It classifies treatments into types based on chemicals—Type 1 (ammonium phosphate) for broad efficacy, Type 2 for alternatives—and mandates minimum retentions, treatment penetration, and leachable thresholds.
Testing under this standard verifies:
- Flame spread index via glow wire or radiant panel methods.
- Critical flux for ignition (>10 kW/m²).
- Smoke density limits during 10-minute exposure.
- No significant afterglow or flaming drips.
BIS licensing requires third-party validation, ensuring panels marked with the ISI seal meet these for public safety. Note: This is informational; consult BIS for latest enforcement details. Non-certified products risk inconsistent performance, especially in monsoon-susceptible interiors.
Measured Performance: Delaying Spread and Reducing Smoke
Certified panels achieve Class 1 flame spread (per IS equivalents), igniting only at edges with charring inward, extending safe exposure by 5-15 minutes versus untreated plywood's rapid engulfment. Smoke output drops by 40-70% in standardized tests, as retardants favor smoldering over turbulent flaming.
In real scenarios—like a kitchen grease fire— this delays flashover, allowing sprinklers or escape. However, no plywood is fireproof; eventual char-through occurs under prolonged heat, emphasizing complementary measures like gypsum boards in walls.
Essential Applications: Kitchens, Offices, and Beyond
In India, where National Building Code (NBC 2016) Part 4 advocates flame-retardant materials in assembly occupancies, commercial kitchens, and high-rises (>15m), these panels suit:
- Kitchens: Modular cabinets near stoves; resists sparks from LPG leaks common in urban homes.
- Offices: Partitions, false ceilings; mitigates wiring short-circuit risks in dense IT hubs like Bengaluru.
- Hotels/Public Spaces: Wall paneling per NBC exit route rules.
- Hospitals/Schools: Furniture to limit smoke inhalation hazards.
Homeowners retrofit wardrobes; contractors specify for tenders mandating IS compliance. Avoid exteriors unless exterior-grade certified, as humidity leaches actives.
Fire Retardant vs. Standard Plywood: Key Differences
| Aspect | Fire Retardant Plywood (IS 5509) | Standard Plywood (MR/BWR/BWP) |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition Time | Delayed (5-10x longer) | Rapid (seconds) |
| Flame Spread | Class 1; chars inward | Class 3-4; surface flames |
| Smoke Production | Low (40-70% less) | High, toxic |
| Treatment | Chemical impregnation | None |
| Use Cases | High-risk interiors | General carpentry |
| Cost Relative | 25-60% higher | Baseline |
Cost uplift arises from chemicals (20-30%), processing, and certification; thinner gauges cost less proportionally.
Buyer Decision Factors in the Indian Market
Architects prioritize BIS marks and test reports; contractors weigh thickness (12-18mm common) against load. Homeowners assess glue grade—pair FR with BWP for kitchens. Regional variations: Coastal dealers stock leaching-resistant variants; northern markets emphasize termite-fire combos.
Verify via:
- ISI stamp with license number.
- Retention certificates from labs.
- Sample glow-wire test (DIY caution advised).
Expect 20-50% premium over BWR; bulk dealer pricing dips in plywood hubs like Yamunanagar.
Longevity and Care in Humid Indian Conditions
Treatments endure 10-20 years indoors if moisture stays below 12%. Seal edges during installation; avoid direct water. Re-treatment rare, but inspect for efflorescence signaling leaching.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is fire retardant plywood truly fireproof?
No—it retards, not prevents, combustion. Provides escape time but requires integrated fire systems.
Does IS 5509 apply nationwide?
Yes, as BIS voluntary standard, increasingly project-mandated in metros.
Can it be used outdoors?
Limited; opt for exterior formulations if available, as interiors leach in rain.
How to spot genuine certification?
Check embossed ISI, CM/L number on BIS site; demand third-party reports.
Impact on painting or finishing?
Minimal; chemicals inert post-cure, accepts laminates/paints standardly.
Want Plywood Suggestions?
Share a few details and a PlyPrice specialist will suggest suitable brands and connect you to responsive dealers.