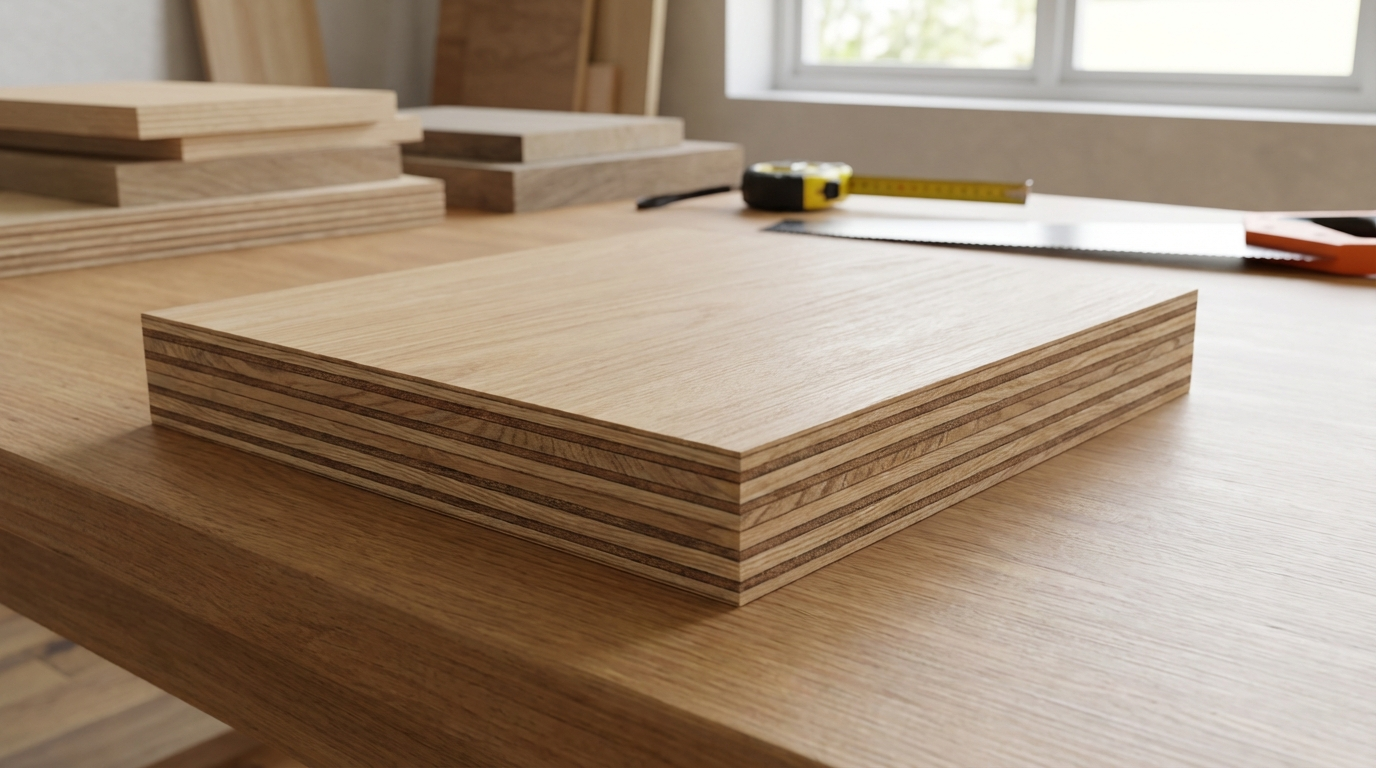
What is BWP Plywood
BWP (Boiling Water Proof) Plywood is marine-grade, IS:710 certified. It withstands 72 hours of boiling water. The ultimate waterproof choice.
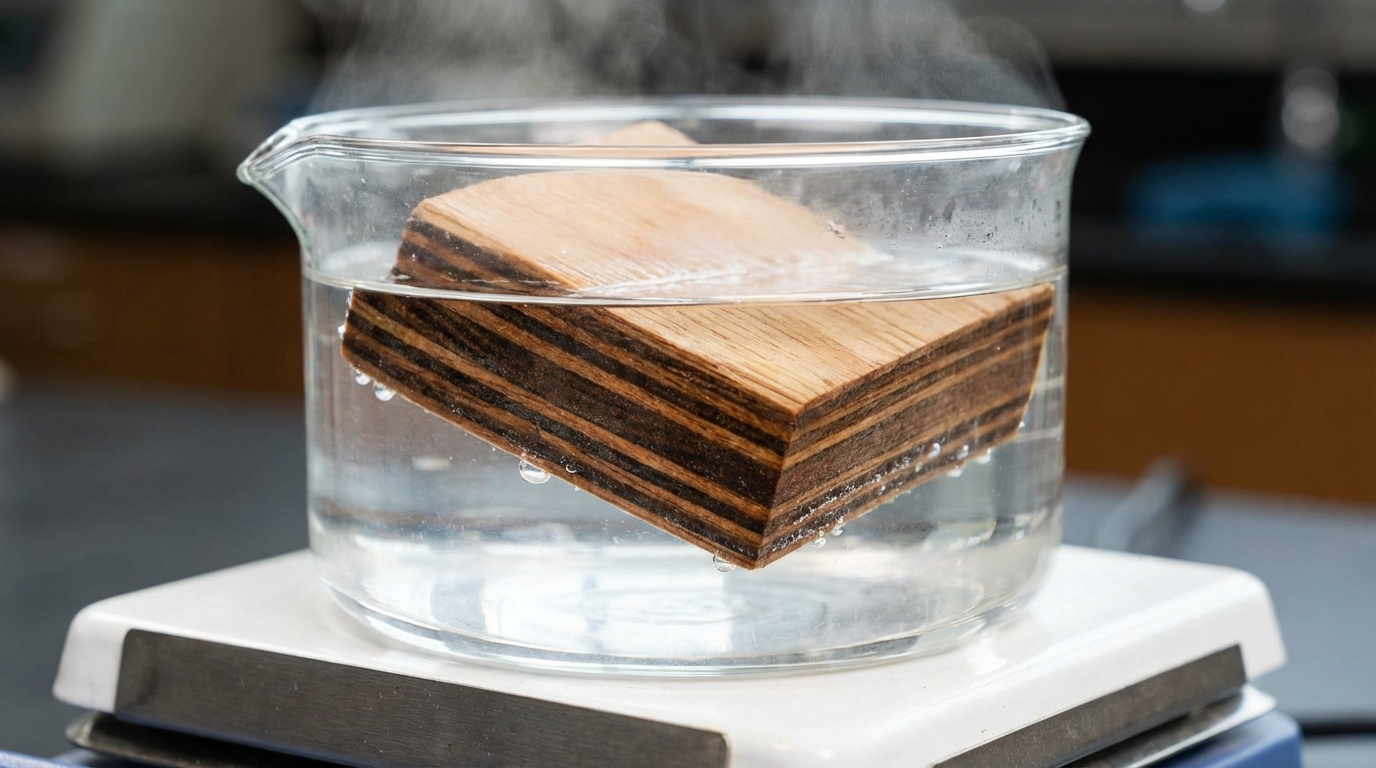

Defining BWP Plywood in Indian Context
BWP plywood, short for Boiling Water Proof, represents the highest tier of moisture-resistant engineered wood available in India. Unlike standard plywood reliant on urea-formaldehyde glues that delaminate under prolonged wetness, BWP uses phenolic resins formulated to endure extreme water exposure. This makes it suitable for environments where submersion or high humidity persists, such as coastal regions during monsoons or submerged structural elements.
Core Composition and Manufacturing Logic
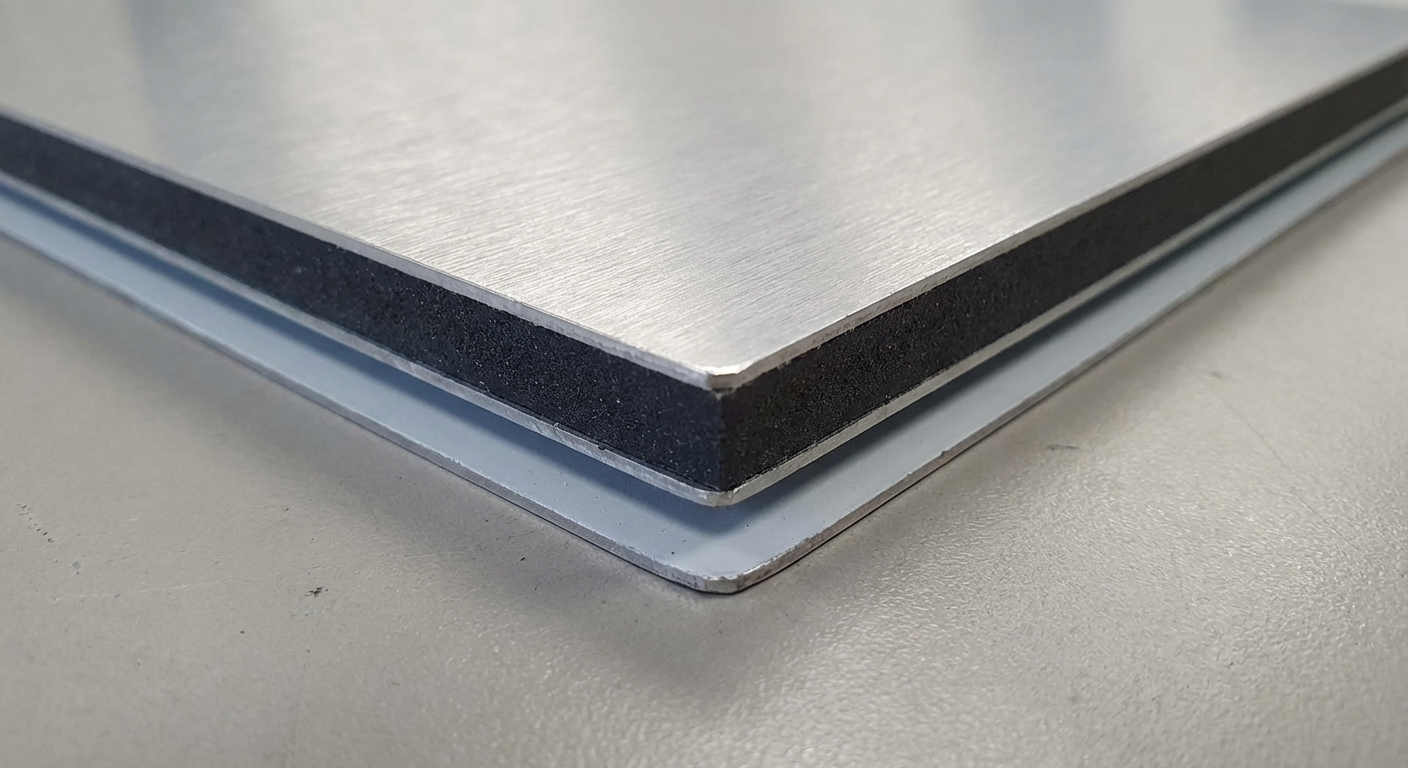
From first principles, plywood layers thin wood veneers cross-bonded with adhesives under heat and pressure. Water resistance hinges on glue type: BWP employs fully synthetic, thermosetting resins that cross-link irreversibly, forming a barrier against hydrolysis. Indian mills produce it from hardwoods like poplar or eucalyptus, with face veneers often graded A or AA for surface quality. Thicknesses range from 4mm to 25mm, balancing rigidity with weight for diverse applications.
IS:710 Certification: The Official Standard
IS:710, issued by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), mandates rigorous testing for BWP classification. Certification requires plywood to maintain structural integrity after boiling in water for 72 hours, followed by drying and reloading to 150% of original strength without failure. Only licensed manufacturers display the BIS hallmark, ensuring compliance with glue boil test, mycological resistance, and dimensional stability norms.
Why IS:710 Matters for Indian Buyers
In India's variable climate—from Kerala’s relentless rains to Mumbai’s humidity—uncertified plywood risks warping or fungal decay within months. Homeowners in high-moisture zones prioritize IS:710 marked sheets to avoid callbacks, while contractors specify it for warranty-backed projects. Architects reference it in specs to align with NBC 2016 guidelines for wet areas, though enforcement varies by municipal oversight.
The 72-Hour Boiling Water Test Demystified
The hallmark test simulates worst-case submersion: plywood samples boil continuously for 72 hours, cool, then undergo shear strength checks. Passing variants retain over 80% delamination resistance compared to dry controls. This exceeds real-world needs—like kitchen counter floods or bathroom steam—but proves glue-film impermeability, critical for marine or exterior uses where intermittent boiling-equivalent stress occurs.
- Pre-test prep: Samples conditioned at 27°C, 65% RH.
- Post-test metrics: Tensile strength > original; no visible separation.
- Practical implication: Survives prolonged exposure without bonding failure, unlike lower grades.
Marine-Grade Designation and Real-World Performance
BWP plywood doubles as marine-grade material per Indian norms, ideal for boat-building, bridges over waterways, or coastal formwork. In humid interiors like Hyderabad apartments or Pune villas, it prevents swelling in modular kitchens exposed to spills. Its density (typically 600-700 kg/m³) resists warping under 90%+ RH, outperforming alternatives in cyclic wet-dry cycles mimicking Indian monsoons.
Limitations in Everyday Use
Despite superiority, BWP isn't omnipotent: UV exposure degrades surface veneers outdoors without sealant; termite vulnerability persists without preservatives. Over-specifying for dry interiors inflates costs unnecessarily, as lower grades suffice there.
BWP Plywood vs Other Grades: Side-by-Side Analysis
Indian plywood grades—MR, BWR, BWP—differ primarily in glue boil tolerance and cost. MR suits dry zones; BWR handles humidity; BWP dominates wet extremes.
| Grade | Glue Type | Boil Test | Typical Use | Cost Relative to MR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR (Moisture Resistant) | Urea-Formaldehyde | Fails after 1-2 hours | Furniture, partitions | Baseline |
| BWR (Boiling Water Resistant) | Modified UF/PF blend | 8 hours | Kitchens, low-humidity exteriors | 20-40% higher |
| BWP (Boiling Water Proof) | Phenolic/Formaldehyde | 72 hours | Marine, bathrooms, monsoons | 50-100% higher |
Cost drivers include resin expense, BIS licensing fees, and regional sourcing—coastal dealers charge premiums due to demand, while inland mills offer 10-20% discounts on bulk.
Practical Applications in Indian Projects
Contractors deploy BWP for shuttering in RCC slabs near water bodies, ensuring reusability post-curing. Interior designers specify 18mm BWP for vanity cabinets in Mumbai sea-facing homes, where steam and splashes test limits. Homeowners in Tier-2 cities like Bhubaneswar opt for it in puja rooms prone to incense humidity, weighing longevity against upfront outlay.
Buyer Decision Framework
Assess exposure risk: >20% time wet? Choose BWP. Budget-constrained? Layer BWR with sealants. Verify hallmarks on edges; reject stamped fakes common in unorganized markets.
Addressing Common Buyer Queries
Is All Marine Plywood BWP?
Not necessarily—marine-grade implies water resistance, but only IS:710 confirms 72-hour boil proof. Generic "waterproof" labels often mask BWR.
Thickness Recommendations?
6-12mm for paneling; 15-19mm for load-bearing; 21mm+ for heavy marine.
Storage and Handling Tips
Elevate stacks off-ground in godowns; cover against direct rain. Indian dealers often bundle with edge-sealing services to extend site life.
Strategic Sourcing Insights
Dealer networks in Gujarat or Kerala hubs yield competitive rates via volume; compare 10+ quotes factoring transport. Architects push branded IS:710 for traceability, but independents suffice for non-critical jobs. Trends show rising HDHMR adoption for interiors, potentially displacing BWP where full submersion isn't risked.
Want Plywood Suggestions?
Share a few details and a PlyPrice specialist will suggest suitable brands and connect you to responsive dealers.